Anti-Inflammatory Foods List (PDF Included)
Looking for an Anti-Inflammatory Foods List PDF to learn which foods may reduce inflammation and promote healing?
Inflammation is the root cause of many chronic illnesses.
Nutrition choices play a role in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms. In my private practice experience as a registered dietitian nutritionist, I see significant symptom score reduction with changes to an anti-inflammatory diet.
In this post, we will review inflammation in the body, tips to reduce inflammation with diet and lifestyle changes, and you can download the Anti-Inflammatory Foods List PDF at the end of this article.
This information is for educational purposes only. As with any medical advice, always check with your doctor or healthcare professional for personal and age-appropriate recommendations.
Want a copy of this article? Click here to download a copy of this article.
Keep reading to learn more.
Table of Contents
Anti-Inflammatory Foods List (PDF Included)
There is a lot of buzz out there about following an anti-inflammatory diet to reduce inflammation, but what is the research showing?
Some of the most popular anti-inflammatory diets include:
- Mediterranean Diet (1, 2, 3)
- DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) (4)
- MIND Diet (Mediterranean-DASH Diet Intervention for Neurodegeneration Delay) (5, 6)
- Blue Zone Diets like Okinawan (7)
- Nordic Diet (8)
- Food Sensitivity Elimination Diet (9, 10, 11)
We will discuss the current evidence-based nutrition and lifestyle information and provide a FREE Anti-Inflammatory Foods List PDF to download.
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is an immune response in the body to fight off foreign invaders.
The inflammatory process is mediated by the regulation of cytokines, prostaglandins, and other mediators (12). When these mediators are released, it signals the immune system to do its job. Too many of these mediators being released can lead to inflammation.
Acute inflammation is beneficial as it helps to heal the body. Once the invaders are destroyed, the immune system can “rest”.

What are the Effects of Chronic Inflammation on the Body?
With chronic inflammation, the inflammatory response continues and wears down the immune system so when the immune system needs to fight off an antigen, it may be less effective, and this may contribute to tissue damage and chronic disease (13, 14).
Some contributors to chronic inflammation include:
- Poor diet with inflammatory foods
- Food allergies and sensitivities
- Being overweight
- Lack of exercise
- Stress
- Sleep deprivation
How an Anti-Inflammatory Diet Can Reduce Inflammation
Food in an anti-inflammatory diet provides important antioxidants, fiber, and nutrients that reduce the inflammatory response, promotes a healthy gut microbiome, and balances blood sugars. Food acts as information for the body, telling our genes what to do.
What is an Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
Inflammation can occur throughout the body and may contribute to symptoms. An anti-inflammatory diet can improve gut health, and reduce symptoms such as fatigue, mood imbalances, chronic pain, and even headaches or migraines.
General tips for to reduce inflammation with diet include:
- Eat a variety of foods.
- Include fresh food as much as possible.
- Minimize your consumption of processed foods and fast food.
- Eat from the rainbow including an abundance of fruits and vegetables (try for 7-9 servings per day).
- Choose organic.
- Consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day.
- Add fatty fish to your meals at least 2 times per week to increase omega 3’s.
- Use healthy oils like olive and avocado oil.
- Flavor foods with herbs and spices.
Michael Pollan has great quotes especially “Eat food. Not too much. Mostly plants” (15).
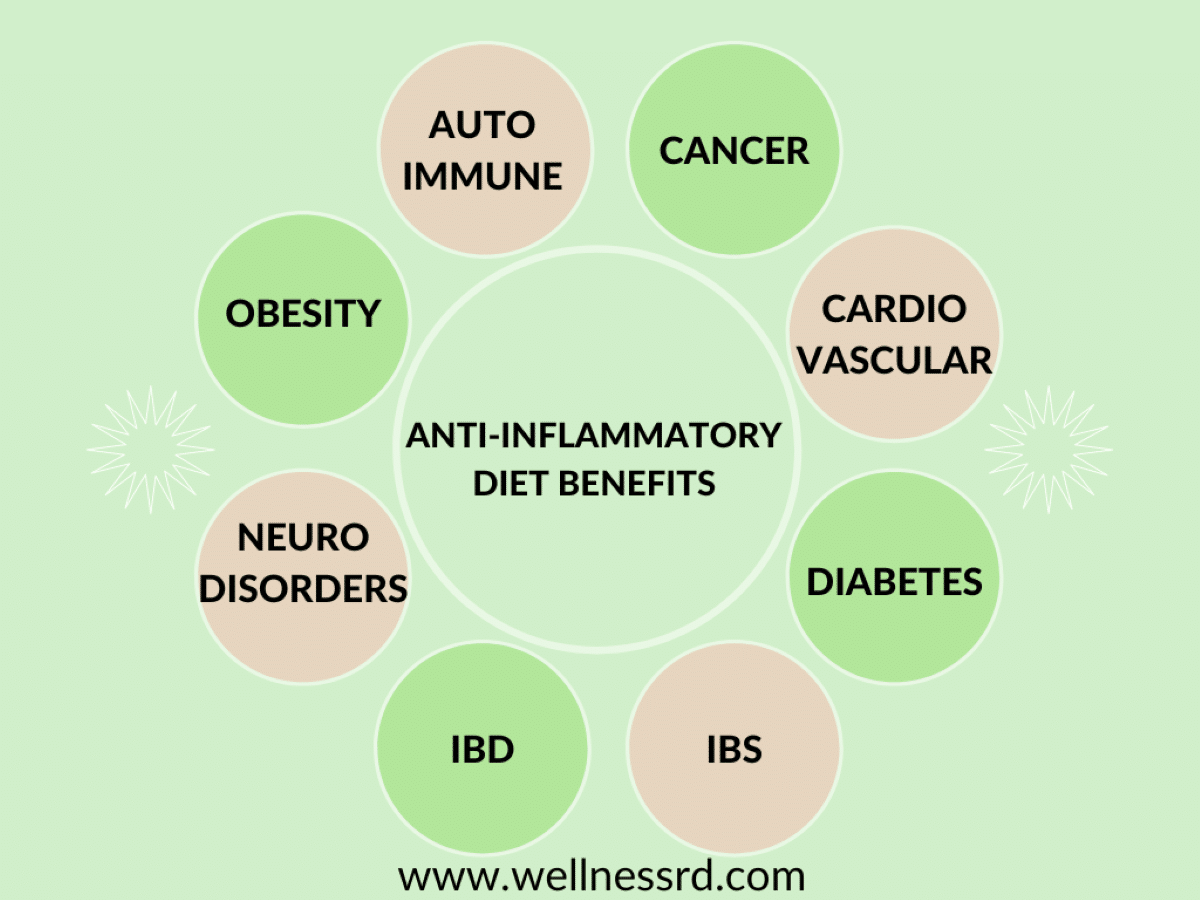
Conditions That Benefit from an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Some of the conditions that benefit from an anti-inflammatory diet are:
- Autoimmune conditions-Rheumatoid arthritis, Multiple sclerosis (16)
- Cancer (17)
- Cardiovascular disease (18)
- Diabetes (19)
- IBS (20, 21)
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD) such as Crohn’s and Ulcerative Colitis (22)
- Neuroinflammation (brain disorders) like Alzheimer’s, ADHD, anxiety, depression, migraine (23, 24, 25)
- Obesity (26)
Benefits of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Optimize Gut Microbiota
Eating anti-inflammatory foods can improve gut microbiota and reduce chronic disease (27). Dysbiosis of the gut may increase the risk of metabolic disorders like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and hyperlipidemia (28). Eliminating inflammatory foods is a first step in the 5R Protocol for gut healing.
Reduce Fatigue
Current research indicates a link between anti-inflammatory diet and fatigue reduction (29).
Decrease Gene Expression
Balancing your diet with anti-inflammatory foods can reduce your inflammatory gene expression (30). Yes, by limiting gene expression you can have less inflammation.
Improve Mood
Studies show an anti-inflammatory diet can improve mood and reduce the risk of depression (31). See my Good Food Good Mood blog for additional info on foods that can boost your mood.
Reduce Chronic Pain
Modifying the diet and incorporating antioxidants which are known to be anti-inflammatory can reduce pain. Some of the compounds to consume are flavonoids, ginger, curcumin, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and taurine (32, 33).
Headache and Migraine Reduction
Inflammatory foods in the diet have an impact on migraine duration, frequency, and severity (34, 35). By choosing anti-inflammatory foods, studies show reduced severity of headaches and migraines (36).
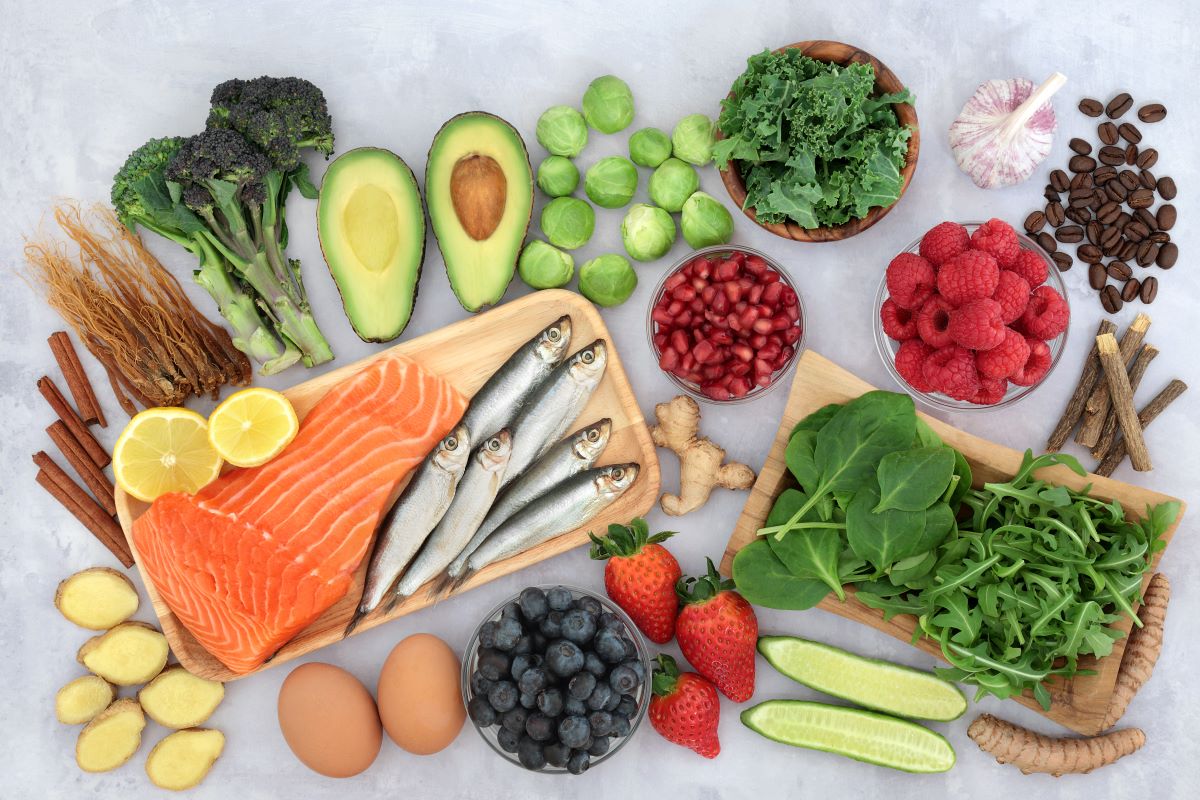
What Foods are on an Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
Vegetables, fruits, and legumes contain phytochemicals which have an anti-inflammatory effect (37).
Some foods to include in a Anti-Inflammatory Diet are:
- Berries
- Oats
- Nuts and seeds
- Olive or avocado oil
- Avocados
- Sweet potato
- Beans and legumes
- Green leafy vegetables
- Cruciferous vegetables
- Omega-3 rich fish (salmon, sardines, trout)
- Alliums like onion, garlic, shallot, leek
- Fresh herbs and spices such as cinnamon, ginger, turmeric

MRT and LEAP: Your Personalized Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Food sensitivities can cause a release of mediators like cytokines, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins which can lead to inflammatory symptoms (38).
For a personalized approach to reducing inflammation, food sensitivity testing has shown to be effective. The MRT (Mediator Release Test) and LEAP protocol can provide a roadmap to create a personalized anti-inflammatory nutrition protocol to reduce inflammation.
In my experience, when the LEAP protocol is followed, a significant symptom reduction score is seen in the first couple weeks.
List of Foods to Avoid on an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
On an anti-inflammatory diet, you should avoid eating processed foods, refined grains, unhealthy oils, excess sugar, and snack foods. If you do not recognize the ingredients on the food product, avoid the food.
Tips for Adding Anti-Inflammatory Foods in Your Diet
Breakfast
- Sprinkle chia or flax seeds to your cereal or smoothie.
- Include berries in your morning meal.
- Make a protein/berry/vegetable smoothie that includes a healthy protein (nut butter, seeds, or protein powder).
- For muffins or pancakes, look for a recipe with oats, nut butters, and seeds.
Lunch and Dinner
- Add beans to your meals (black beans, garbanzos, kidney beans, lentils, pinto beans).
- Sprinkle avocado or olive oil over your vegetables or salad and toss with some seeds.
- Add canned salmon or tuna to your meals- incorporating low mercury, high omega-3 fish (salmon, mackerel, anchovies, sardines, herring) 2-3 times per week.
- Cook with fresh grated ginger, garlic, leek, onions, or shallots as tolerated.
- Add cinnamon to your hot beverage (tea, coffee).
- Use fresh herbs and spices to add phytonutrients and flavor to your favorite dish.
- Mash an avocado with lemon or lime and add some herbs.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Inflammation
Exercise
The anti-inflammatory effects of regular exercise (30 minutes of exercise, 5 days/week) can reduce your risk of chronic disease (39).
Sleep
Optimal sleep is essential for gut and brain health (40, 41). Nutritional factors including magnesium and vitamin B12 can also influence sleep.
Mindfulness and Stress Management
Mindfulness is “being in the present moment”. It strengthens the brain and reduces stress.
A meta-analytic review of mindfulness-based interventions resulted in improved psychiatric disorder symptoms and showed low but significant changes in inflammatory health markers (42).
Final Thoughts
Chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and chronic disease.
Conditions that may benefit from an anti-inflammatory diet are autoimmune conditions, cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, IBS, IBD, neuroinflammation, and obesity.
Benefits of an anti-inflammatory diet include improving gut health, reducing fatigue, decreasing gene expression, improving mood, reducing chronic pain, and decreasing migraines and headaches.
MRT and the LEAP protocol can create a personalized anti-inflammatory diet roadmap.
Exercise, sleep, and mindfulness are important additions to an anti-inflammatory lifestyle.
Download the Anti-Inflammatory Foods List PDF here.
Read the blog for more information on functional nutrition.
Test don’t guess.
Contact me to schedule an appointment to review your personalized nutritional health.
© Amy Archer RDN, CLT, CHWC